Basic Authentication
It is a mechanism to authenticate access to the resource over HTTP.
Credentials are sent in the request headers in the form of Authorization: Basic <base64 encoded username and password>.
Ever seen this page?
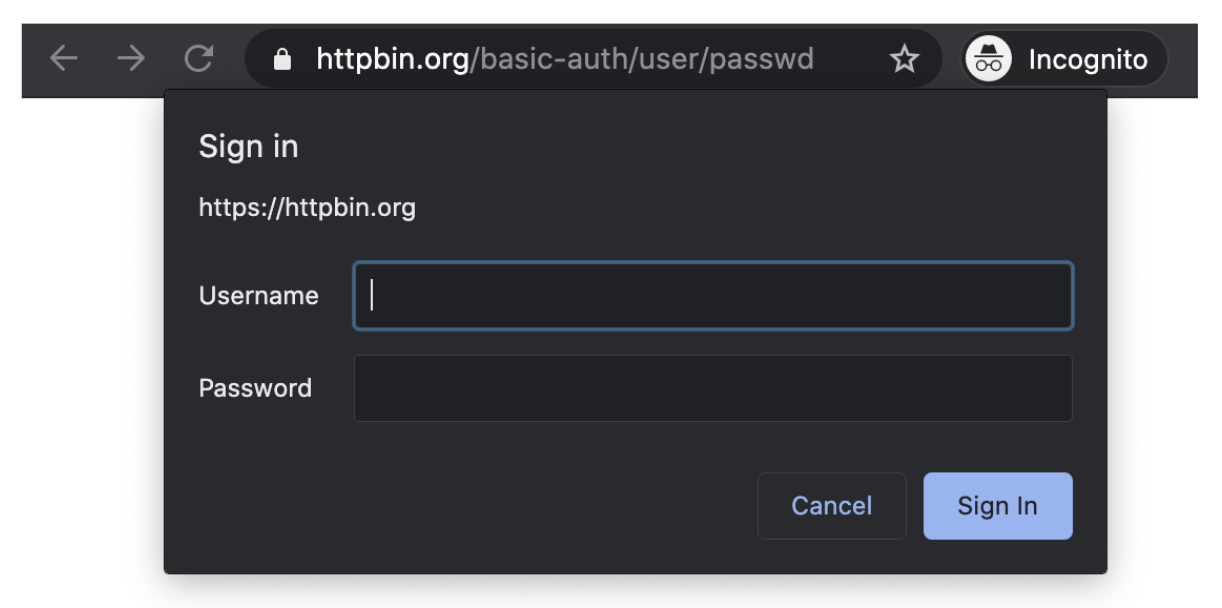
This is basic authentication in play!
How does it work?
- Client tries to access some protected URL or other resource.
- Server checks if the request contains the
Authorizationheader with valid username and password.- (Success) If it exists and is valid, the server sends the requested resource and
status: 200. - (Go to step 3) If credentials don't exists or are invalid, the server sends
status: 401and theWWW-Authenticateheader with theBasic realm="Restricted Area"value.
- (Success) If it exists and is valid, the server sends the requested resource and
- The client receives the
401status and theWWW-Authenticateheader and shows the login form. - The client fills in the form and sends the request again. The credentials are encoded using
base64and sent in theAuthorizationheader.base64(username:password). - (Go to step 2) Continue cycle.
Note:
- Basic auth is not considered secure unless used with TSL/HTTPS. Because anyone can intercept the request and decode the credentials.
- Basic auth can also be used in APIs, but in that case it is just like normal token-based authentication.